Internal Link vs External Link: Understanding Their Role in SEO
Did you know that internal and external links play a vital role in how your website ranks on Google? Internal links help users navigate your site, while external links build credibility by connecting to trusted sources. Together, they form the backbone of a solid SEO strategy. But knowing when and how to use them can make all the difference in improving your site’s performance.
In this blog, we’ll break down the differences between internal and external links, their benefits, types and explain you how to use them effectively. Whether you’re a beginner or just looking to polish your SEO skills, this guide is for you.
What Are Internal Links?
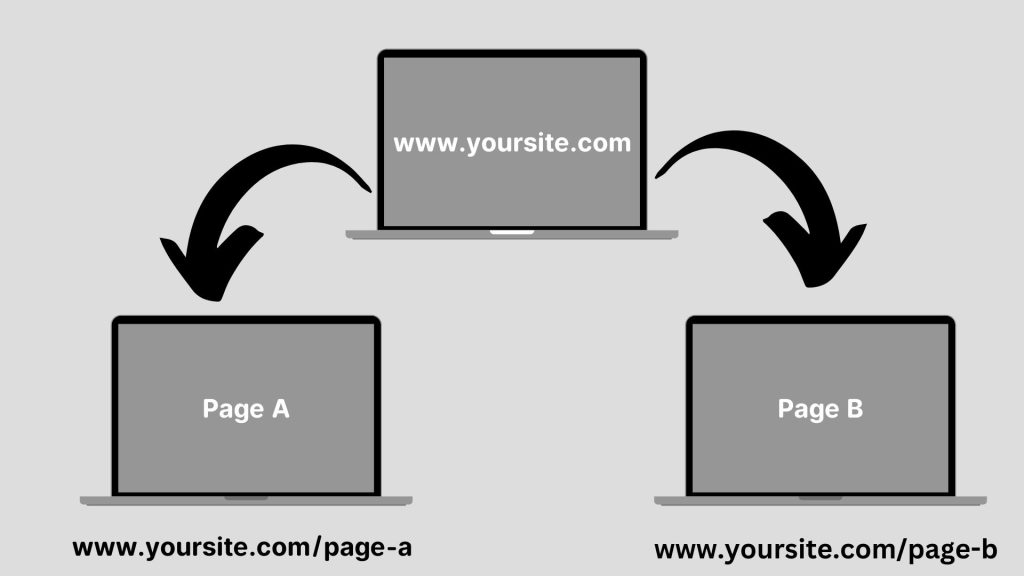
Internal links are hyperlinks that connect one page of a website to another page on the same site. Think of them as a way to guide visitors deeper into your website. For example, if you’re reading a blog about “SEO Basics” and it links to another page of the same website explaining “Keyword Research,” that’s an internal link.
Benefits of Internal Links
- Improved Site Navigation: Internal links help users find relevant content quickly, improving their user experience.
- SEO Value: They distribute link equity or link juice across your website, helping search engines prioritize important pages.
- Encouraging Engagement: By linking to related content, you keep visitors on your site longer, reducing bounce rates.
Example:
Imagine you own an e-commerce store selling fitness gear. On your blog about “Best Workouts for Beginners,” you include an internal link to your product page for yoga mats. This not only helps users but also signals to search engines that the product page is valuable.
Best Practices for Internal Links
- Use Descriptive Anchor Text Anchor text is the clickable part of a hyperlink. Use clear and descriptive text to indicate where the link will take users. For example, instead of “Click here,” use “Learn about keyword research techniques.”
- Link to Relevant Pages Ensure the internal links you use are meaningful and related to the content. For example, a blog about “SEO Strategies” could link to a guide on “On-Page Optimization.”
- Avoid Overloading Pages Don’t clutter a page with too many internal links. Stick to 2-5 per page, depending on the content length.
- Audit Regularly Perform regular link audits to ensure all internal links are functional and relevant.
What Are External Links?
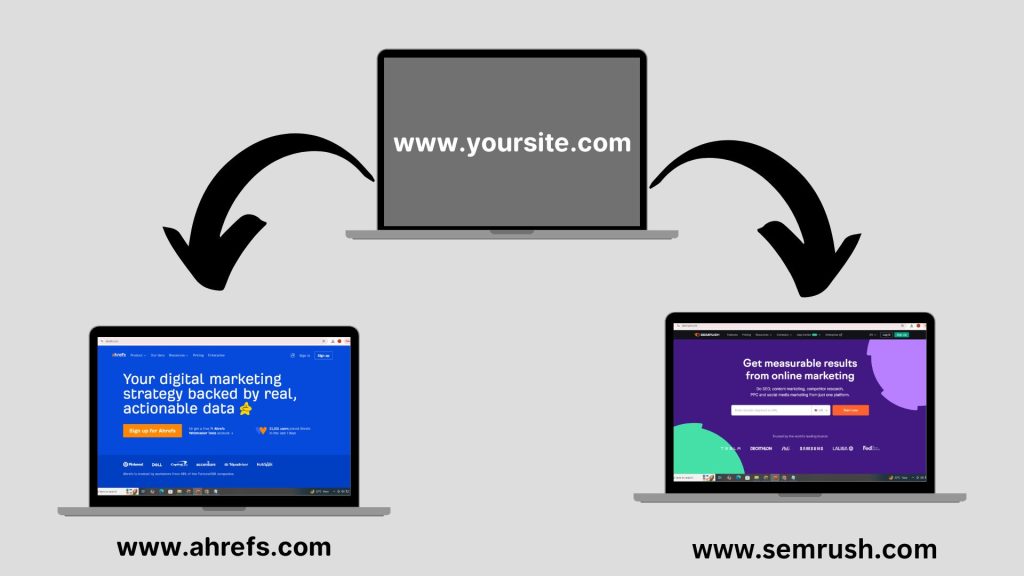
External links are hyperlinks that point from your website to another website. They provide additional resources or references for your readers. For instance, if your blog discusses “SEO Tools” and links to a tool like Ahrefs or Semrush, that’s an external link.
Example:
If you click on Ahrefs or Semrush on the above paragraph, you will be redirected to another website. That’s called external link
Benefits of External Links
- Builds Credibility: Linking to authoritative sites shows you’ve done your research, making your content more trustworthy.
- Enhances User Experience: External links provide valuable resources that help readers dive deeper into a topic.
- SEO Impact: Google considers external links as a sign that your content is well-referenced and informative.
Best Practices for External Links
- Choose Authoritative Sources Always link to trusted websites with high domain authority. For example, linking to industry leaders like Moz or HubSpot adds credibility.
- Use Nofollow Tags When Necessary If you’re linking to a paid or sponsored site, add a “nofollow” tag to avoid passing link equity.
- Ensure Links Open in New Tabs External links should open in a new tab so users can explore without leaving your site entirely.
- Check for Broken Links Regularly check external links to ensure they’re still active and pointing to the intended resource.
Types Of External Links
When creating links, you can assign attributes to guide how search engines treat them. Here’s a simple explanation of each type of external links:
Do-follow Links
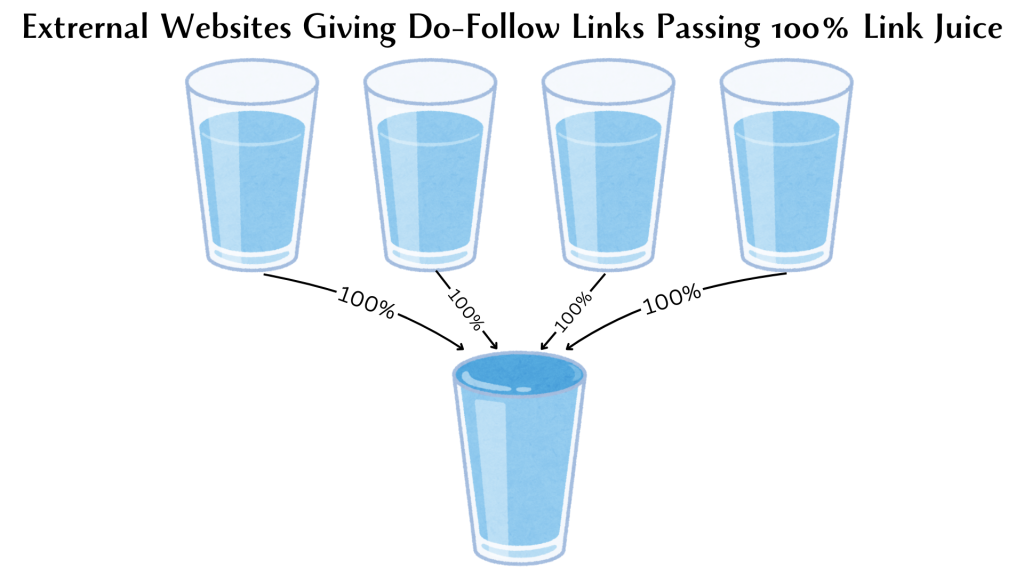
These links pass SEO value, often referred to as “link juice,” to the destination site. This means that search engines recognize the link as a signal of trust and authority.
Make sure to link the relevant content that is useful for the reader and the site must be genuine and authoritative. If the linked page is not relevant to your content or the site is not authoritative, it will hurt your website’s SEO.
Example:
If you write a blog about SEO strategies and link to a detailed guide on keyword research, search engines will follow that link and boost the SEO ranking of the linked website. This is why do-follow links are valuable for improving the visibility of a webpage.
<a href=”https://example.com/keyword-research-guide”>Read this keyword research guide</a>
Note: If a link contains the attribute rel="follow" or has no attribute at all, it is considered a do-follow backlink.
No-Follow Links
These links do not pass SEO value to the linked site. They are used when you want to include a link but don’t necessarily want to influence the linked website’s search rankings. This is achieved by adding a rel="nofollow" attribute to the link.
Example:
If you’re writing about blogging tips and want to refer another website without passing SEO value: No-follow links are particularly useful when linking to a relevant content available on other website but you are unsure about the website authoritativeness or its credibility.
<a href=”https://www.exampleblog.com” rel=”nofollow”>Visit Example Blog</a>
Sponsored links
These links are used to indicate paid or promotional content. These links include the rel="sponsored" attribute, which tells search engines that the link was placed as part of a sponsorship or advertisement.
Example:
If a company pays you to promote their product, service or any content on your blog, you would use a sponsored link to comply with search engine guidelines. This ensures transparency and prevents search engines from treating the link as an organic endorsement.
<a href=”https://www.examplesite.com” rel=”sponsored”>Check out this service</a>
Quick Comparison Table
| Type | Passes SEO Value? | Use Case | Example Attribute |
|---|---|---|---|
| Do-Follow | Yes | Organic, trusted links. | <a href="url"> |
| No-Follow | No | Untrusted or user-generated links. | <a href="url" rel="nofollow"> |
| Sponsored | No | Paid or promotional content. | <a href="url" rel="sponsored"> |
Key Differences Between Internal and External Links
| Feature | Internal Links | External Links |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Direct users to other pages on your site | Direct users to other websites |
| Control | Fully controlled by you | Almost no control over the linked content |
| SEO Impact | Distributes link equity within your website | Improves credibility by connecting to trusted sources |
| User Experience | Improves site navigation | Provides additional resources for readers |
Conclusion
Internal and external links aren’t just technical SEO tools—they’re essential elements of a user-friendly and high-performing website. Internal links guide users through your site and boost page authority, while external links build trust by connecting to credible sources.
Now that you know the differences and best practices, it’s time to put them into action. Audit your site’s links today to maximize SEO and enhance user experience.
Need help optimizing your website’s links? Contact our team of SEO experts and take your site to the next level!
FAQs
1. Do Internal or External Links Help More with SEO?
Both are important. Internal links improve site structure and navigation, while external links build credibility and authority.
2. How Many Internal Links Should I Use Per Page?
Stick to 2-5 internal links, depending on the length and relevance of your content.
3. What Happens If an External Link Breaks?
Broken external links create a poor user experience and can hurt your SEO. Regularly audit your links using tools like Screaming Frog.